近日,Nature旗下免疫学期刊Cellular & Molecular Immunology在线发表了我院医学院•整合医学学院史丽云课题组的最新研究成果The metabolic regulator Lamtor5 suppresses inflammatory signaling via regulating mTOR-mediated TLR4 degradation。
Toll样受体(Toll like receptor, TLR)是一类重要的模式识别受体,其表达及活化水平与机体免疫稳态维持密切相关,TLR过度活化可引发炎症、自身免疫性疾病等。LAMTOR5是晚期内体/溶酶体适配器以及MAPK和哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(late endosomal/lysosomal adaptor and MAPK and mammalian target of Rapamycin activator, LAMTOR)复合物的成员之一,参与氨基酸诱导的mTORC1活化。但是目前为止,有关LAMTOR相关分子参与TLR及其介导的炎症信号通路的研究极少。史丽云课题组研究发现LAMTOR5分子受细菌脂多糖(lipopolysaccharide, LPS)诱导而上调,并显著抑制LPS诱导的炎症因子的分泌和炎症信号通路的活化;进一步研究显示LAMTOR5分子与内化的TLR4受体分子发生特异性结合,二者共定位于自噬溶酶体上,由此阻止mTOR在其上的结合和活化,引发后续转录因子(transcription factor EB, TFEB)入核而上调自噬溶酶体相关基因表达,从而促进TLR4的自噬降解及其介导的炎症信号通路的阻断。该研究首次揭示了LAMTOR5分子通过mTOR/TFEB轴参与TLR4介导的炎症信号通路调控的作用及其机制,为临床治疗内毒素血症等炎症性疾病提供新的思路。
论文链接:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41423-019-0281-6
DOI: 10.1038/s41423-019-0281-6
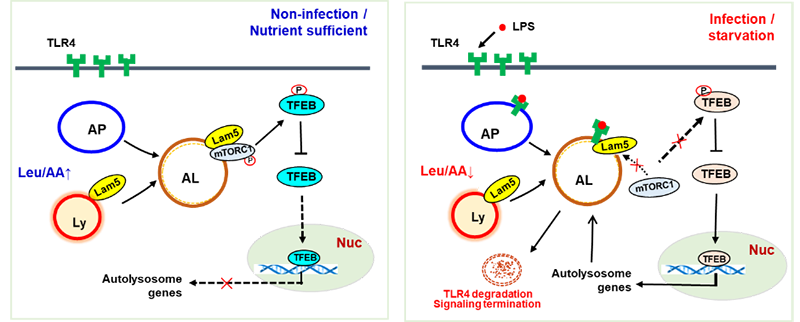
A proposed working model indicating that Lamtor5 plays dual roles in both associating with/recruiting TLR4 and regulating the TFEB-driven autolysosomal pathway, thereby contributing to the autophagic degradation of TLR4 and inflammation termination. AA amino acid, AP autophagosome, AL autolysosome, Ly lysosome, Lam5 Lamtor5, Leu leucine, Nuc nucleus.
